SSH Tunnel
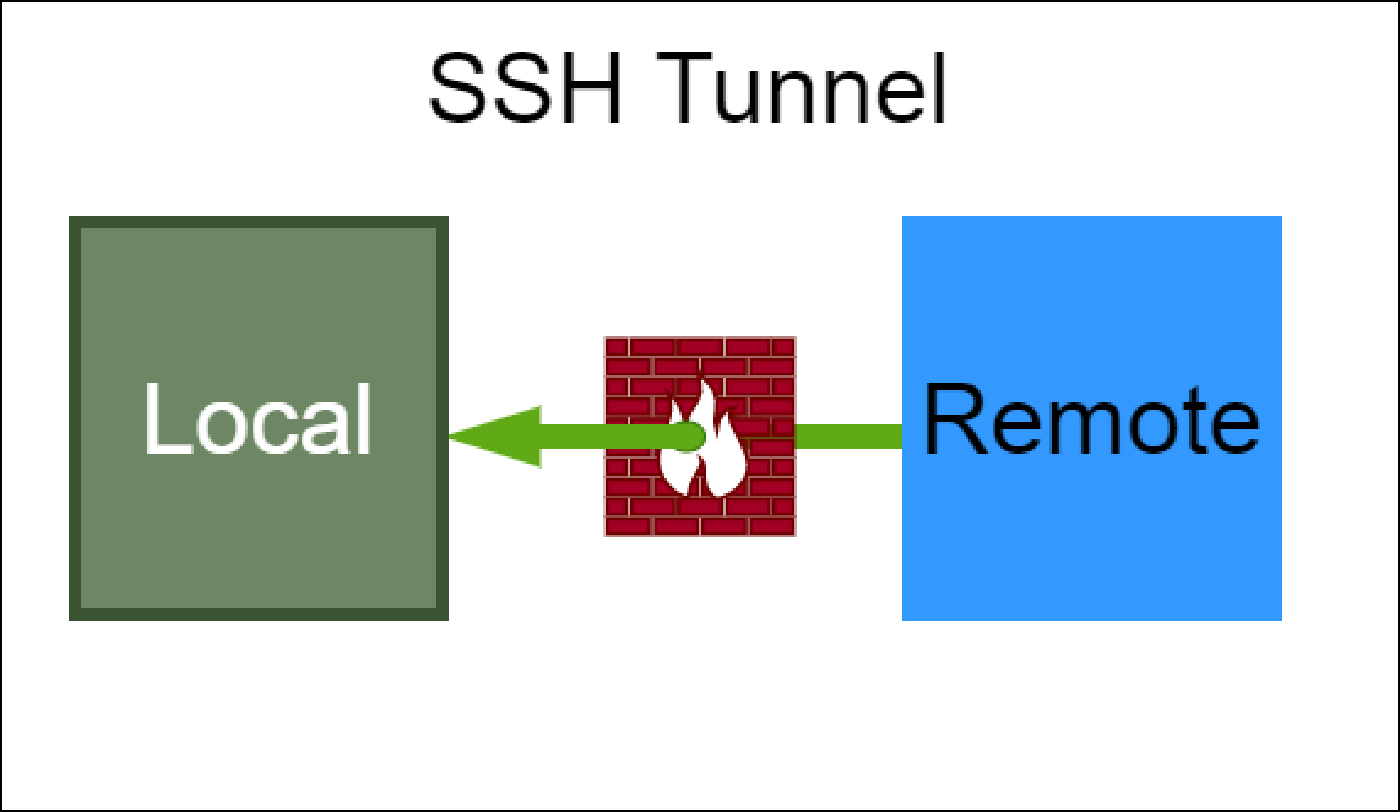
SSH Tunnel
How to setup a basic SSH tunnel to access remote server resources that may be blocked by a firewall or simply inaccessible over the internet.
Understanding SSH Tunnels
Remote server that is running on port 80. Access this service from local computer, but a firewall is in the way.
Setup
| Host Type | IP Address | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Local | localhost | |
| Remote | 192.168.0.6 | Internal IP address of the local service |
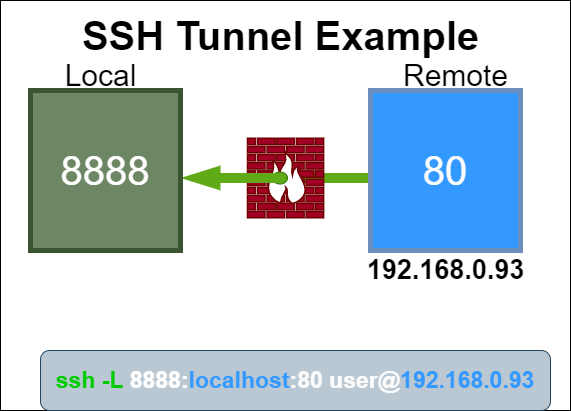
To bypass the firewall restrictions, send the remote service over the SSH port via a tunnel.
SSH Tunnel Example
Confirm listening ports
Remote
Remote server running web server on port 80 and ssh on port 22.
> netstat -ntl
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN
From the remote run the following command to establish a SSH tunnel:
> ssh -N -L localhost:8888:localhost:80 root@192.168.0.93
-Nis a flag to just forward ports and not execute remote commands-Lforwards local connections to the remote side- localhost is the host on the local machine that will bind to the remote service
- 8888 is the port that the local machine will listen on
- localhost is the internal IP address of the remote service
- 80 is the port of the remote service
- root is the SSH user of the remote server
- 192.168.0.93 is the public IP address of the remote server
The remote service at localhost:80 will be accessible on the local machine at http://127.0.0.1:8888.
-p 2222 of the remote server.Confirm listening ports
Local
Local is now established local connection port 8888 to remote system 192.168.0.93:80.
> netstat -ntl
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:8888 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
Shorthand
Remote command execution or pseudo terminal will be allocated for this connection.
> ssh -L 8888:localhost:80 root@192.168.0.93
Change the port number for other services.
- Don’t need to include localhost of the local machine because it is default
- Default SSH port is 22, so don’t need to specify this
-Nflag is optional. Functionality will be the same
Might be able to trace tunnel through lsof. Need to explore more.
> lsof -a -i -c '/^ssh$/'
Summary
Greate way to access remote services that are private and not exposed to the internt or that are running behind a firewall to access this service from local computer.
Check out:
Related Posts
2023 Phoenix VMUG UserCon
Introduction: The recent 2023 Phoenix VMUG UserCon brought together some like-minded people in the field, with discussions ranging from VMware technologies to best practices for optimizing existing systems.
Read moreRed Hat User Group Insights, Ansible Automation Platform, and ITSM Integration
Introduction: This blog post aims to summarize the key takeaways from this informative workshop. At the recent Red Hat User Group workshop on Red Hat Insights, Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform, and their integration with management (ITSM) systems, such as ServiceNow, provided valuable insights into how these technologies work together.
Read moreRobocopy Examples
Robocopy Examples Robocopy has many command line options and it can be overwhelming to know which commands to use. In this post, we will take a look at how to ues robocopy to copy, mirror, purge Files and Folders.
Read more