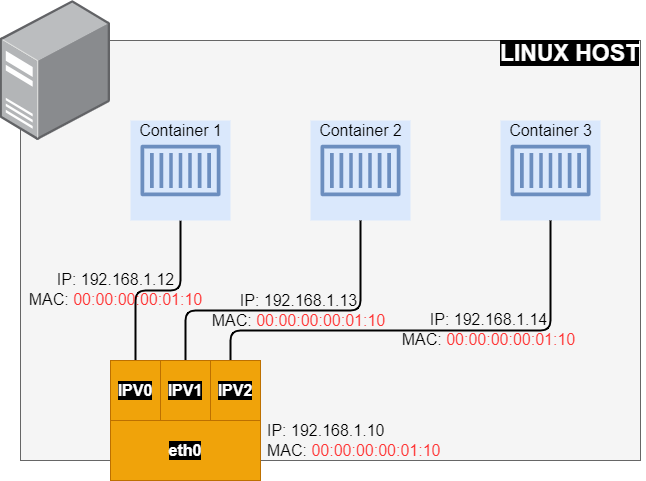
Docker IPvlan Networks
Use IPvlan networks
IPvlan driver gives control over both IPv4 and IPv6 addressing. The VLAN driver gives administrators control of layer 2 VLAN tagging and even IPvlan L3 routing for use of direct network integration.
Prerequisites
- The examples on this post are all single host
- All examples can be performed on a single host running Docker. Any example using a sub-interface like
eth0.10can be replaced witheth0or any other valid parent interface on the Docker host. Sub-interfaces with a.arecreatedon the fly.-o parentinterfaces can also be left out of thedocker network createall together and the driver will create adummyinterface that will enable local host connectivity to perform the examples. - Kernel requirements:
- To check your current kernel version, use
uname -r - IPvlan Linux kernel v4.2+ (support for earlier kernels exists but is buggy)
- To check your current kernel version, use
IPvlan L2 mode example usage
An example of the IPvlan L2 mode topology is shown in the following. The driver is specified with -d driver_name option. In this case -d ipvlan.
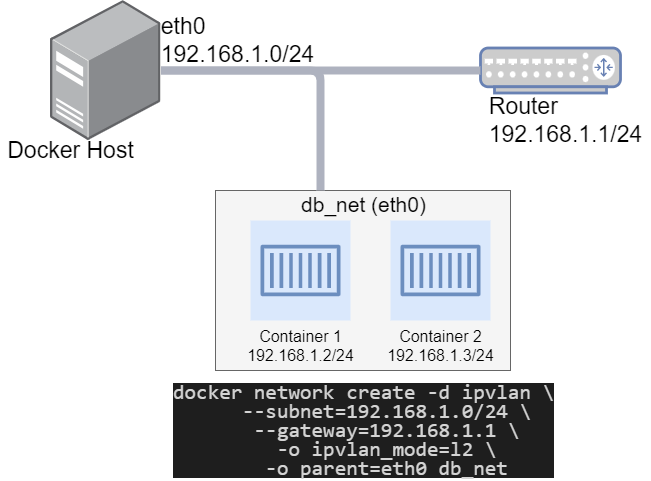
Simple IPvlan L2 Mode Example
The parent interface in the next example -o parent=eth0 is configured as follows:
ip addr show eth0
3: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.1.10/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global eth0
Use the network from the host’s interface as the --subnet in the docker network create. The container will be attached to the same network as the host interface as set via the -o parent= option.
Create the IPvlan network and run a container attaching to it:
docker network create -d ipvlan \
--subnet=192.168.1.0/24 \
--gateway=192.168.1.1 \
-o ipvlan_mode=l2 \
-o parent=eth0 db_net
Start a container on the db_net network
docker run --net=db_net -it --rm alpine /bin/sh
Docker Compose Example
Making things a bit easier with a docker compose file. To illustrate the above, we will use a two Docker Containers.
The gateway can be only specified under version 2.
Create the docker-compose.yml file:
version: '2'
services:
container1:
image: alpine
container_name: container1
restart: unless-stopped
tty: true
networks:
- db_net
container2:
image: alpine
container_name: container2
tty: true
networks:
- db_net
networks:
db_net:
driver: ipvlan
driver_opts:
ipvlan_mode: l2
parent: eth0
ipam:
config:
- subnet: 192.168.1.0/24
gateway: 192.168.1.1
From within the directory Run: docker-compose up -d
Validate Containers Up
Showing command and output in the code samples.
Using Docker Inspect
Check the container process to see if two containers are up and running:
docker ps --format \
"table {{.ID}}\t{{.Status}}\t{{.Names}}"
CONTAINER ID STATUS NAMES
58129dfe9dda Up 3 minutes container2
39ad7928071a Up 3 minutes container1
Check Docker networks:
docker network ls
NETWORK ID NAME DRIVER SCOPE
2d44dd74beb6 bridge bridge local
bd777dfcc50c host host local
2a2a001fdf18 ipvlan_db_net ipvlan local
156a09c3d2f5 none null local
How to Get A Docker Container IP Address:
Using Docker Inspect on container ID 39ad7928071a
docker inspect -f '{{range .NetworkSettings.Networks}}{{.IPAddress}}{{end}}'
192.168.1.12
Using the Network ID 2a2a001fdf18
docker network inspect -f \
'{{range .IPAM.Config}}{{.Subnet}}{{end}}' 2a2a001fdf18
192.168.1.0/24
Look up each Container’s IP individually:
Based on the ipvlan_db_net Network ID 2a2a001fdf18 assuming jq is instaled.
docker network inspect -f \
'{{json .Containers}}' 2a2a001fdf18 | \
jq '.[] | .Name + ":" + .IPv4Address'
"container1:192.168.1.12/24"
"container2:192.168.1.13/24"
Using Docker exec
In the following example we will work with container1.
Using the exec to run commands in a running container, but can execute an interactive sh shell on the container if want to execute additional commands.
docker exec -it container1 sh
From Docker host ping remote server.
docker exec container1 ping 192.168.1.20
Remote host capture packets tcpdump
tcpdump -e -ni eth0 icmp
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on eth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes
... TRUNCATED OUTPUT ...
15:39:26.006311 00:00:00:00:01:10 > 00:00:00:00:01:20, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 192.168.1.12 > 192.168.1.20: ICMP echo request, id 19, seq 4, length 64
15:39:26.006427 00:00:00:00:01:20 > 00:00:00:00:01:10, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 192.168.1.20 > 192.168.1.12: ICMP echo reply, id 19, seq 4, length 64
... TRUNCATED OUTPUT ...
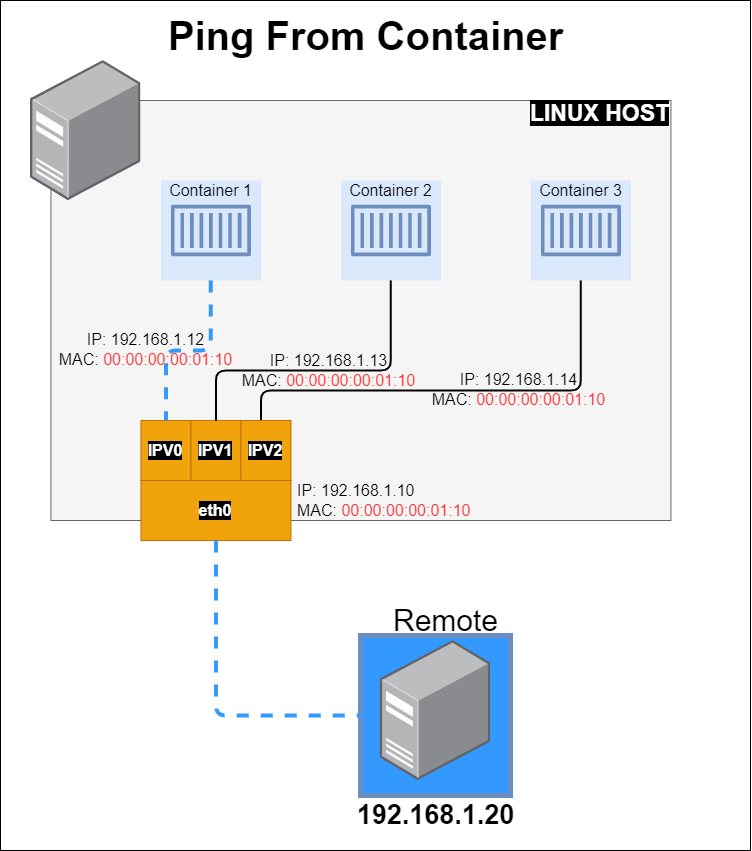
MAC from container: HWaddr 00:00:00:00:01:10
docker exec container1 ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:00:00:00:01:10
inet addr:192.168.1.12 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
... TRUNCATED OUTPUT ...
MAC from host: ether 00:00:00:00:01:10
ifconfig eth0
eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.1.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.1.255
ether 00:00:00:00:01:10 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
... TRUNCATED OUTPUT ...
Stop Containers
Remove containers and network with docker-compose down
Summary
The VLAN driver builds on top of that in giving administrator complete control of layer 2 VLAN tagging and even IPvlan L3 routing for users interested in underlay network integration.
Below are some considerations when using IPvlan:
| PARAMETER | IPvlan | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Network Interface Compatibility | Limited Mac Address | ||
| Hardware Performance | Hardware Performance | ||
| Security | Unknown | ||
| Implementation | Needs Advanced Router Configuration | ||
Next in the Series:
Related Posts
2023 Phoenix VMUG UserCon
Introduction: The recent 2023 Phoenix VMUG UserCon brought together some like-minded people in the field, with discussions ranging from VMware technologies to best practices for optimizing existing systems.
Read moreRed Hat User Group Insights, Ansible Automation Platform, and ITSM Integration
Introduction: This blog post aims to summarize the key takeaways from this informative workshop. At the recent Red Hat User Group workshop on Red Hat Insights, Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform, and their integration with management (ITSM) systems, such as ServiceNow, provided valuable insights into how these technologies work together.
Read moreRobocopy Examples
Robocopy Examples Robocopy has many command line options and it can be overwhelming to know which commands to use. In this post, we will take a look at how to ues robocopy to copy, mirror, purge Files and Folders.
Read more